
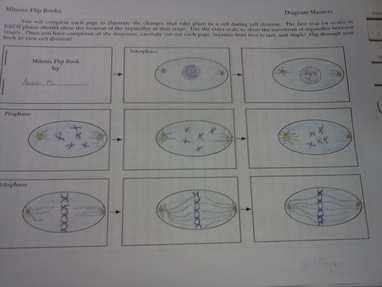
Mitosis ‘“ separation of chromosomes into two identical sets of daughter cells Meiosis II – second part of the meiotic process with the production of four haploid cells from the two haploid cells Telophase I – arrival of chromosomes to the poles with each daughter cell containing half the number of chromosomesĦ. Metaphase I – Homologous pairs move along the metaphase plate, kinetochore microtubules from both centrioles attach to the homologous chromosomes align along an equatorial plane.Ĥ.Ěnaphase I – shortening of microtubules, pulling of chromosomes toward opposing poles, forming two haploid setsĥ. Prophase I ‘“ pairing of homologous chromosome pair and recombination (crossing over) occursģ. Meiosis I ‘“ separation of homologous chromosomes and production of two haploid cells (23 chromosomes, N in humans)Ģ. Without meiosis the fertilization would result in zygote with twice the number of the parent.ġ. Meiosis influence stable sexual reproduction by halving of ploidy or chromosome count.
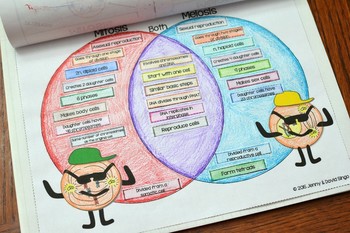

Gametes formations occur in animal cell and meiosis is necessary for sexual reproduction which occurs in eukaryotes. Meiosis is a reductional cell division where the number of chromosomes is divided into half. Telophase- de-condensation of chromosomes and surrounded by nuclear membranes, formation of cleavage furrow. Metaphase- alignment of chromosomes at the metaphase plateĥ.Ğarly anaphase- shortening of kinetochore microtubulesĦ. Prometaphase- degradation of the nuclear membrane, attachment of microtubules to kinetochoresĤ. Prophase ‘“ formation of centrosomes, condensation of chromatinģ. Interface -where cell prepares for cell division and it also includes three other phases such as G1 (growth), S (synthesis), and G2 (second gap)Ģ. Basically, in mitosis the mother cell divides into two daughter cells which are genetically identical to each other and to the parent cell.ġ. In mitosis chromosomes separates and form into two identical sets of daughter nuclei, and it is followed by cytokinesis (division of cytoplasm). Meiosis and Mitosis describe cell division in eukaryotic cells when the chromosome separates.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
